When selecting a plastic pyrolysis plant, the decision often boils down to choosing between a batch and a continuous system. Each configuration offers distinct advantages and operational characteristics. Understanding the differences between these two types of plants is crucial for making an informed decision. Various factors, such as production capacity, energy efficiency, and long-term operational costs, play a role in determining which plant is better suited for specific business needs. In this comparison, we will examine key aspects to help guide the selection process.

Production Capacity and Scalability
The small scale plastic pyrolysis plant operate in defined cycles, with a clear start and stop process for each cycle. Typically, the raw materials are loaded into the reactor, the system is heated to the required temperature, and once the pyrolysis process is completed, the reactor is cooled before unloading. This cyclical nature means batch plants are best suited for small to medium-scale operations. The downtime between cycles limits overall throughput, which can affect businesses that aim for higher production volumes.
On the other hand, continuous pyrolysis plants run non-stop, with raw materials being fed into the system while pyrolyzed products are simultaneously discharged. This uninterrupted operation makes continuous plants ideal for large-scale businesses with high production demands. Scalability is a significant advantage of continuous systems, as they allow for expanded capacity without extensive downtime. For enterprises seeking consistent output, continuous plants provide a better solution.
Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption is a critical factor in evaluating the operational cost of pyrolysis plants. Batch pyrolysis plants, with their start-stop operation, often require more energy per cycle due to the need for frequent reheating. The system cools down after each cycle, necessitating energy for reheating when production resumes. Over time, this can result in higher fuel or electricity consumption, making the batch process less efficient in terms of energy use.
In contrast, continuous pyrolysis plants are designed to maintain a steady operational temperature throughout. Once the system reaches the required temperature, it remains stable, significantly reducing the energy needed for reheating. The constant operation of continuous plants ensures better energy utilization, which can translate to lower operating costs in the long run. For businesses aiming to optimize energy expenditure, continuous Beston plastic pyrolysis plant offers a more energy-efficient alternative.
Operational Complexity
Batch pyrolysis plants are simpler to operate and maintain, making them a practical choice for businesses with limited technical expertise. The start-stop nature allows operators to easily inspect the plant during downtimes, perform maintenance, and address any issues that may arise. Additionally, batch systems generally require fewer skilled workers to manage, which can reduce labor costs.
However, continuous pyrolysis plants demand a higher level of automation and technical skill to manage effectively. The uninterrupted process requires constant monitoring to ensure smooth operation, as any malfunction could disrupt the entire system. Maintenance in continuous plants is also more complex, as it often needs to be performed without halting the operation. Therefore, businesses that opt for continuous systems must be prepared for higher operational complexity and the potential need for specialized technicians.
Investment and Equipment Cost
When considering the initial investment, batch pyrolysis plants are typically more affordable, as they are smaller in scale and require less sophisticated equipment. For businesses with limited capital, batch systems offer a lower entry cost. The affordability of batch plants often makes them a favorable option for startups or smaller enterprises looking to enter the pyrolysis industry.
Continuous pyrolysis plants, on the other hand, come with a higher price tag. The additional cost stems from the more advanced technology, larger capacity, and automation systems required for continuous operation. Although the initial investment is significantly higher, the long-term financial benefits of increased production capacity and lower energy costs can offset the initial expenditure. The plastic pyrolysis machine price will vary depending on the plant’s capacity, level of automation, and the specific technology employed, so it’s essential to consider long-term gains when evaluating investment costs.
Maintenance and Downtime
In terms of maintenance, batch plants offer a clear advantage with easier access to equipment during downtimes between production cycles. This simplicity allows operators to address mechanical issues, replace parts, or perform regular servicing without interrupting production for extended periods.
Continuous pyrolysis plants, by design, limit the time available for maintenance due to their non-stop operation. Any downtime can lead to production delays and potentially greater financial losses. As such, continuous systems often incorporate redundant components or scheduled maintenance windows to mitigate the impact of necessary repairs. Choosing a reliable pyrolysis plant manufacturer that offers robust maintenance support can reduce the operational risks associated with continuous systems.
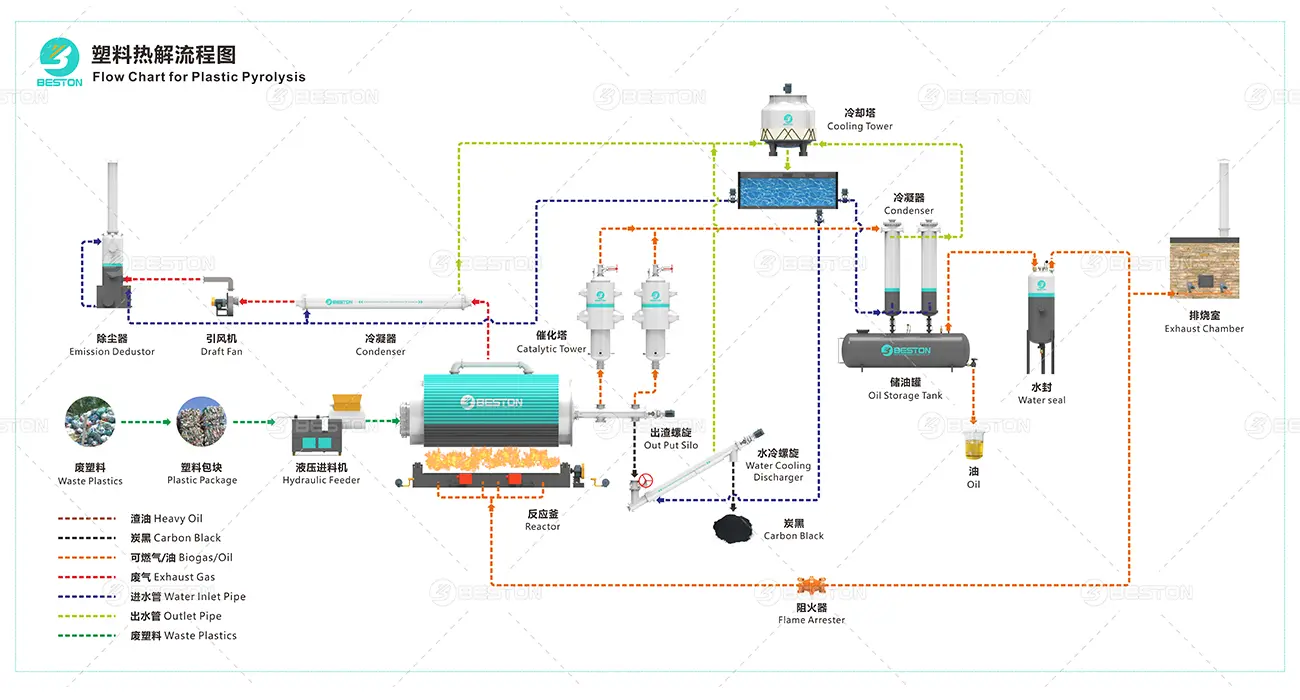
Conclusion
The choice between a batch and continuous pyrolysis plant ultimately depends on specific business needs. Batch plants offer simplicity, lower investment costs, and flexibility, making them suitable for small to medium-sized operations. In contrast, continuous pyrolysis plants provide higher capacity, energy efficiency, and scalability, which can justify their higher price and operational complexity. Evaluating factors such as production goals, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements will help businesses make an informed decision that aligns with their long-term objectives. By selecting the right plant and pyrolysis reactor manufacturers, businesses can maximize their return on investment while minimizing operational challenges.