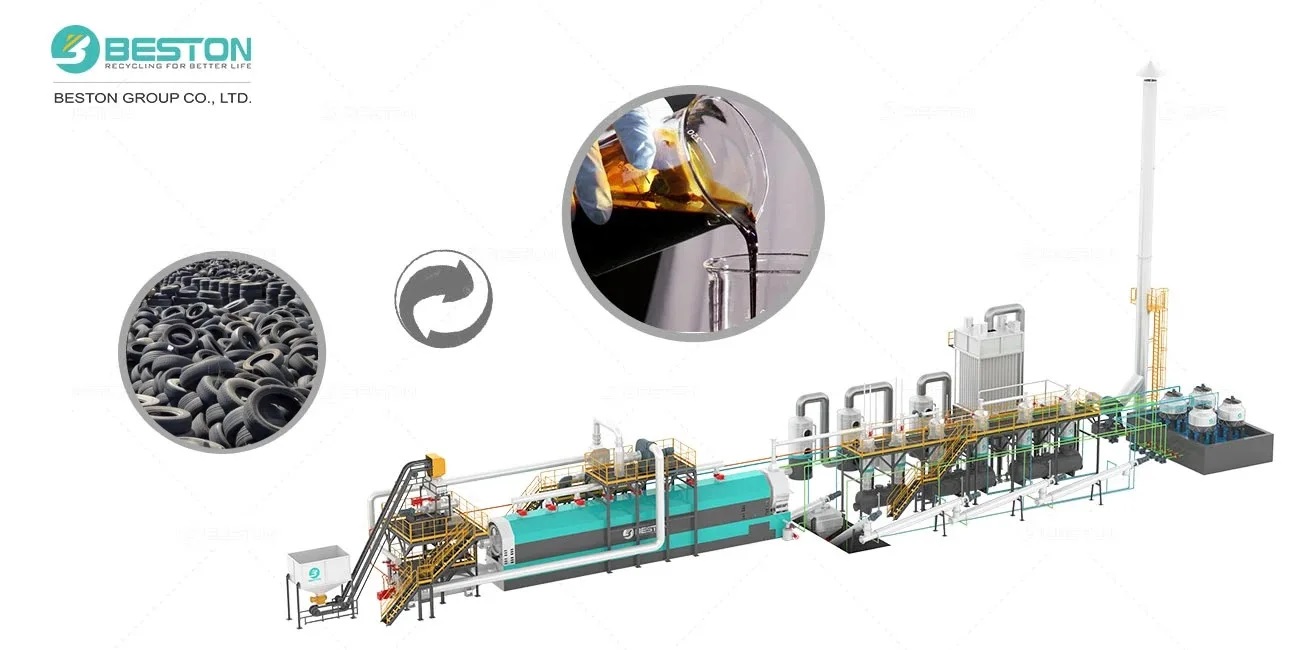
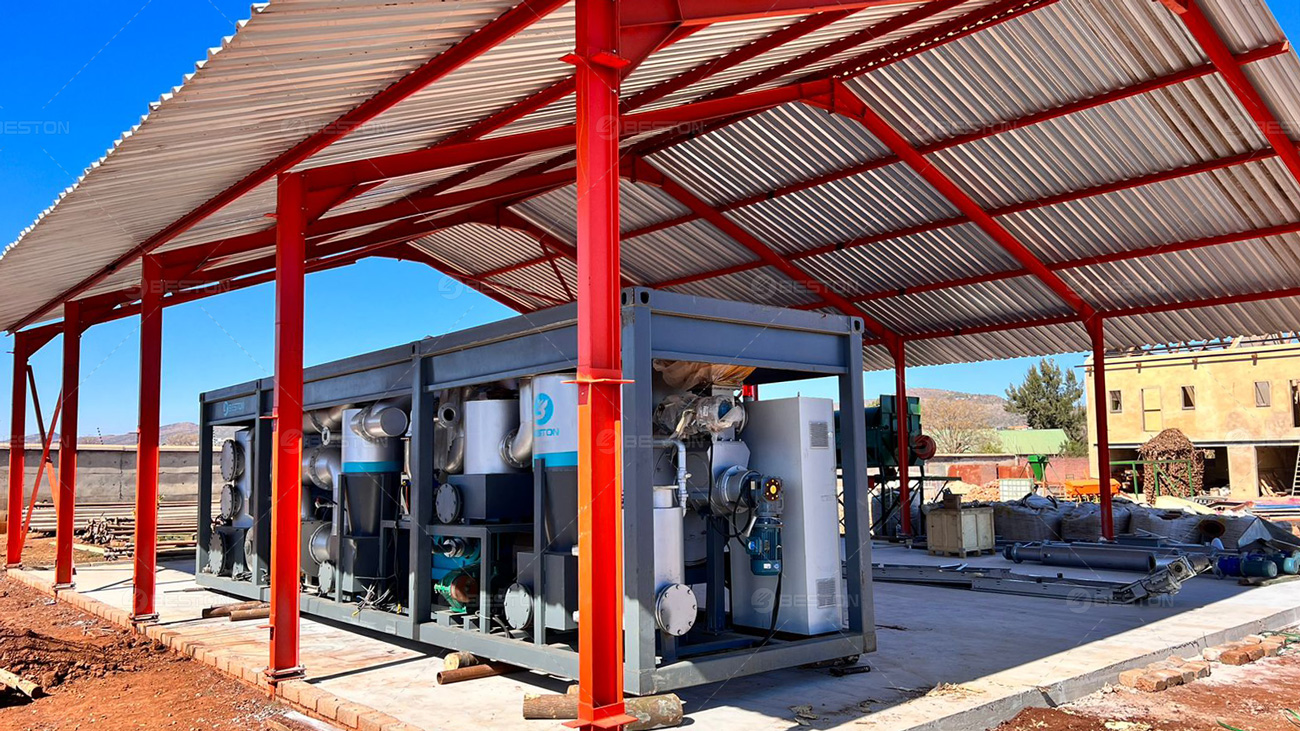
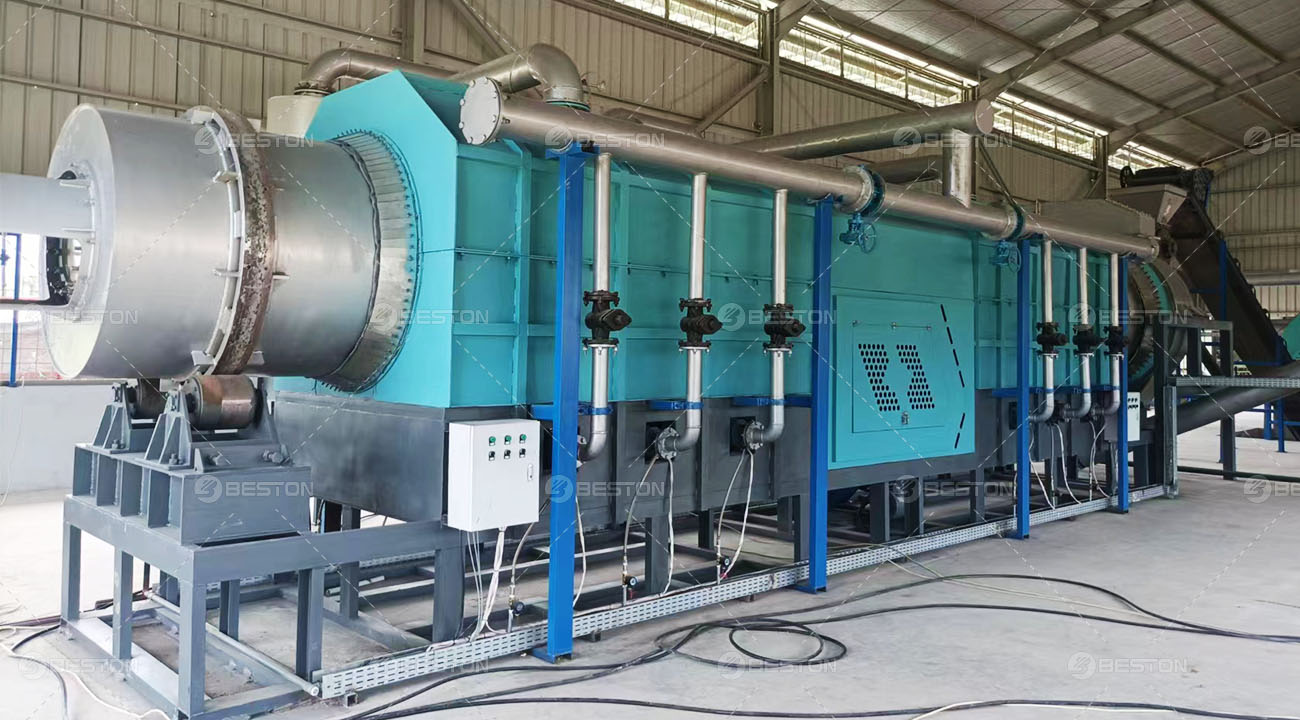
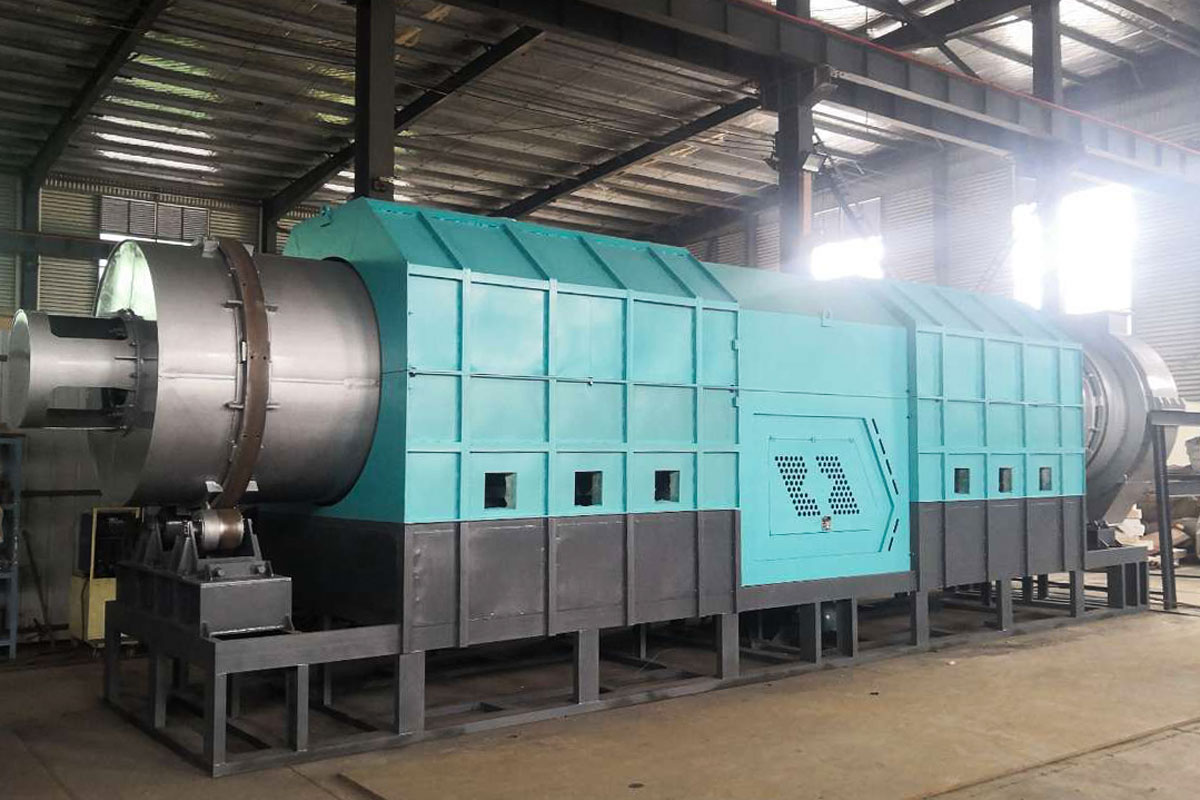
Elevating Throughput and Thermal Stability
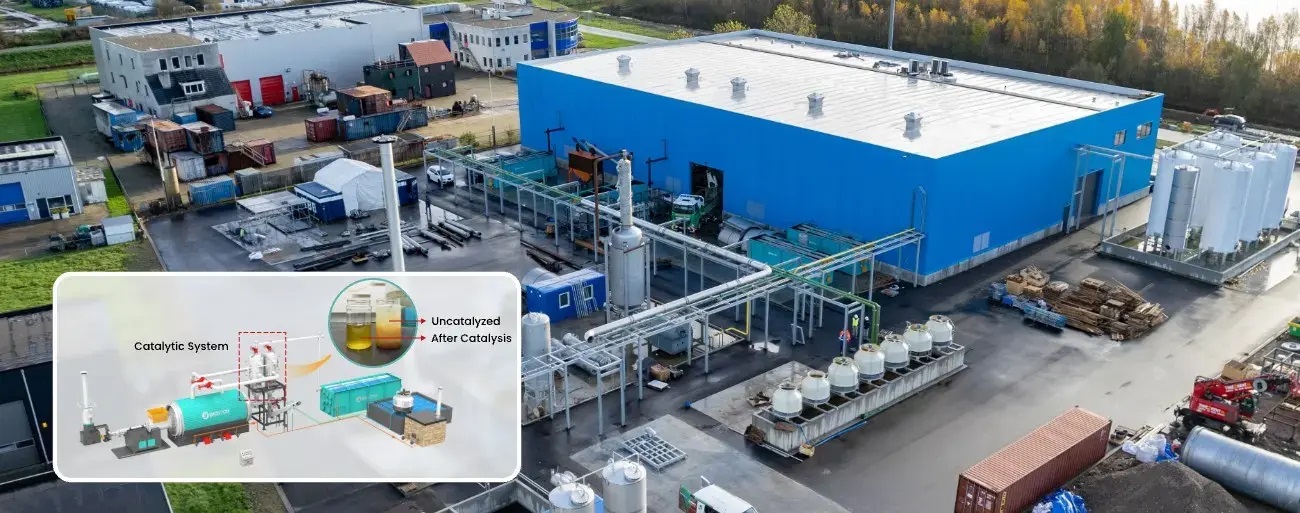
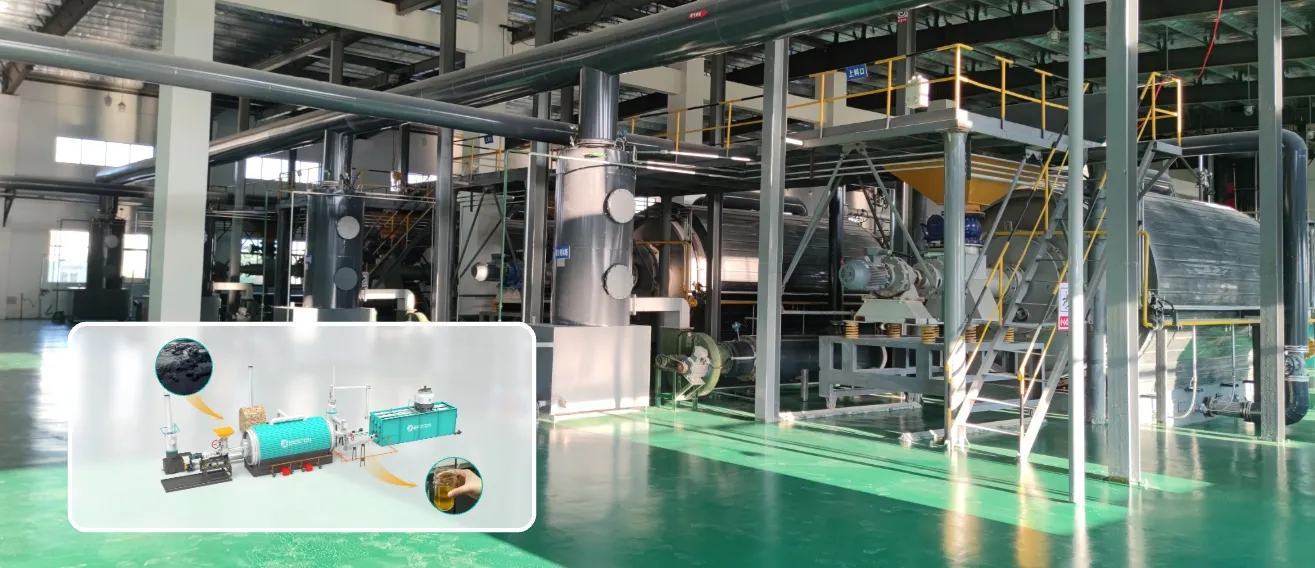
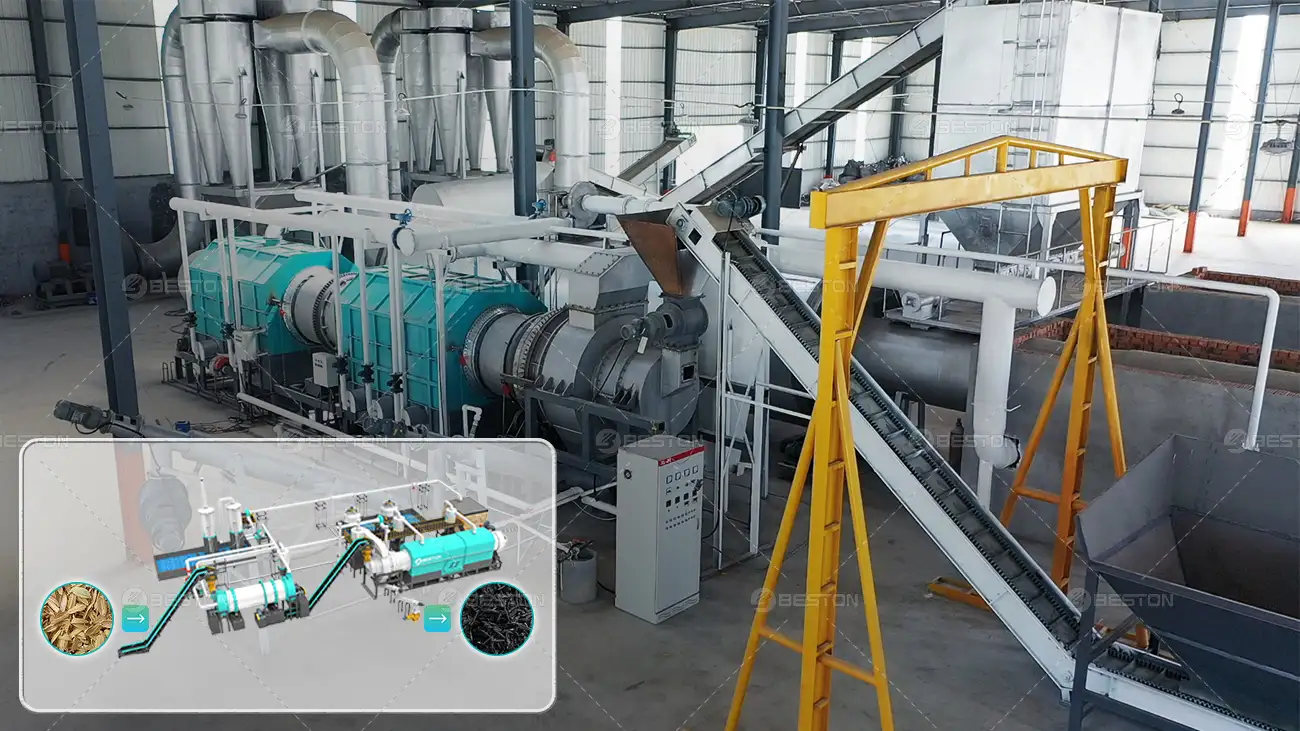
Continuous plastic pyrolysis has emerged as a pivotal pathway for transforming heterogeneous polymeric waste into reusable hydrocarbons. Upgrading the underlying technology introduces significant advancements in throughput and thermal stability. Unlike batch-oriented configurations, a modern continuous system sustains an uninterrupted feed of shredded plastics into the reactor vessel, minimizing thermal cycling and reducing mechanical stress on internal components. This operational steadiness enhances the repeatability of reaction kinetics and suppresses undesirable thermal fluctuations that often degrade product quality.
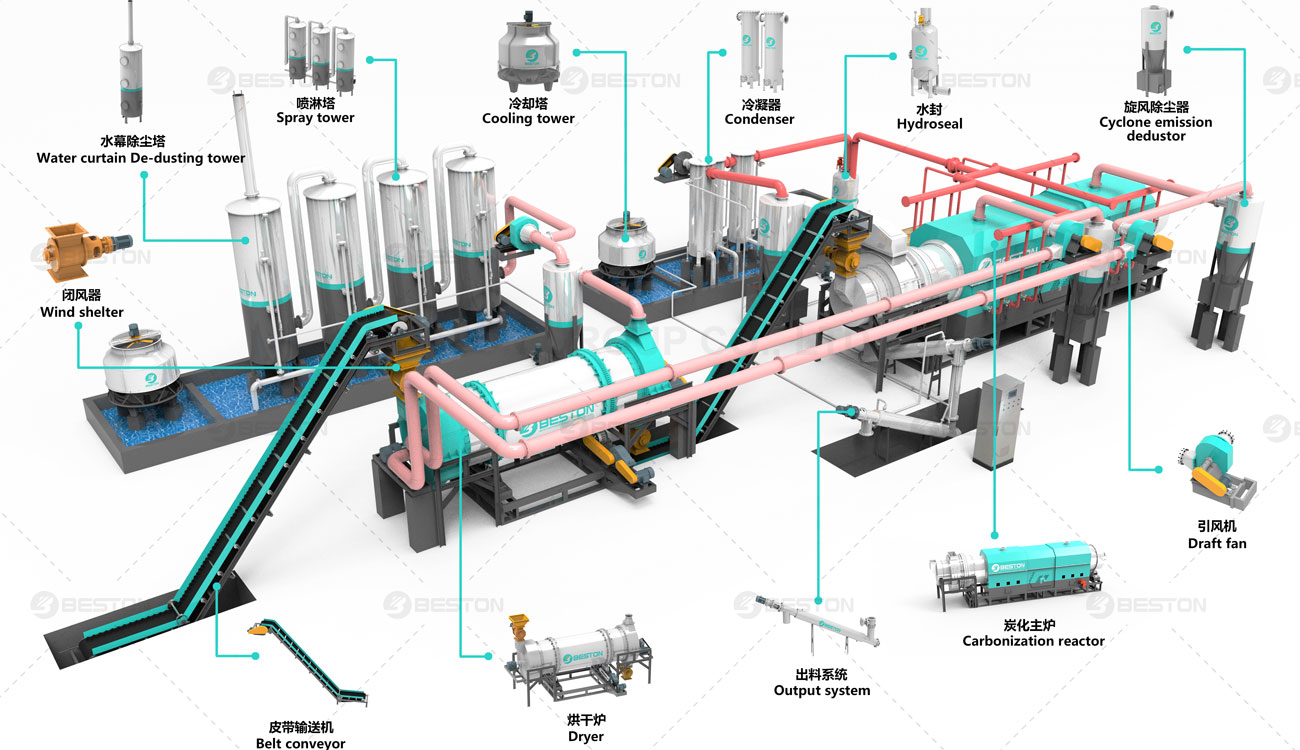
Within an optimized plastic pyrolysis plant, improved reactor metallurgy and advanced insulation materials reinforce temperature homogeneity across the reaction chamber. Even subtle improvements in thermal uniformity can elevate the yield of condensable vapors, fostering a more consistent distribution of pyro-oil fractions. Short sentences matter. Stability matters more. These cumulative refinements strengthen the long-term reliability and energy efficiency of the installation.

Intensifying Feedstock Flexibility and Conversion Efficiency
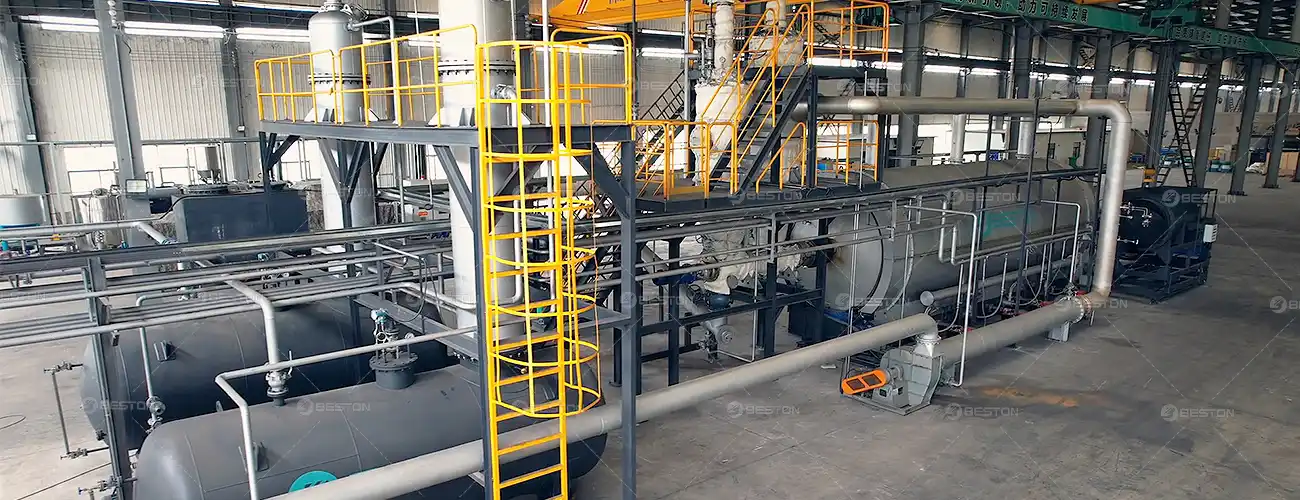
Modernization of continuous pyrolysis systems brings sharper adaptability to fluctuating feedstock compositions. Plastic waste streams seldom remain homogeneous. They mix polyolefins, polystyrene, PET residues, and multilayer films. Enhanced pretreatment modules—such as automated density separators, improved shredders, and low-fouling drying units—allow the facility to rationalize these inputs with minimal manual intervention. As a result, conversion pathways become more tolerant to contaminants, enabling broader resource recovery in regions facing inconsistent waste supplies.
Catalytic upgrades further augment this resilience. High-surface-area catalysts, engineered with specialized pore distributions, accelerate depolymerization at lower activation energies. The reaction proceeds with greater selectivity, reducing char formation and boosting overall hydrocarbon recovery. In a modernized continuous pyrolysis plant, these catalytic elements can be replaced or regenerated through modular trays, preserving uptime while maintaining optimal conversion performance. The synergy of enhanced feedstock management and catalytic precision pushes conversion efficiency toward new benchmarks.
Refining Output Quality and Hydrocarbon Yield
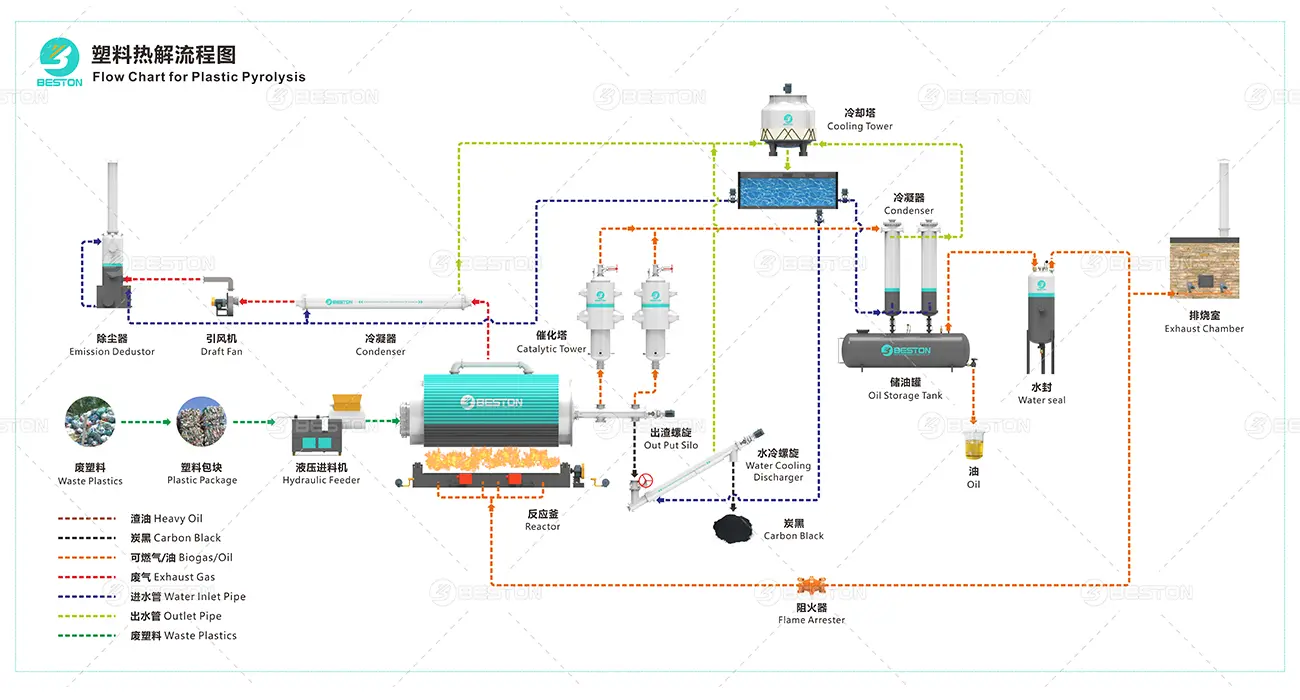
Quality control stands as a principal motivation for upgrading continuous pyrolysis technology. Advanced condensation trains equipped with multistage heat exchangers isolate specific hydrocarbon fractions with greater fidelity. The resulting pyro-oil features narrower boiling ranges, lower sulfur content, and reduced polymeric residuals. This refined output simplifies downstream hydrotreatment and blending processes, making the recovered oil more compatible with existing petrochemical value chains.
Moreover, upgraded gas purification systems—leveraging membrane separators and sorbent columns—distill non-condensable gases into cleaner fuel streams. These gases can reenter the pyrolysis reactor’s heating circuit, reducing auxiliary fuel demand and cutting operating expenditures. Meanwhile, solid residues experience improved processing through automated ash handling and magnetic separation, which divert recoverable metals for resale. The cumulative effect is elevated output yield, reduced waste, and enhanced revenue diversification.
Strengthening Environmental Stewardship and Regulatory Alignment
Environmental performance plays an increasingly central role in decision-making for thermal recycling technologies. Upgrading continuous pyrolysis systems directly advances emissions mitigation. State-of-the-art thermal oxidizers neutralize volatile organic compounds and reduce odor emissions. Flue gas scrubbers equipped with alkaline misting and fine-particle filtration handle acidic off-gases and particulates with greater rigor, positioning the facility to comply with tightening regulatory thresholds.
Energy optimization also contributes to ecological stewardship. Recovered syngas and waste heat are recirculated through high-efficiency heat exchangers, diminishing dependence on grid electricity or external fuels. Some installations integrate heat-to-power modules, turning waste thermal energy into electrical output for auxiliary operations. When aggregated, these improvements materially lower the carbon footprint of the entire process. In regions where environmental accreditation is essential for project financing, such upgrades provide strategic advantages. If you require environmentally compliant solutions, please contact Beston Group.
Enhancing Operational Continuity and Cost Predictability
Continuous systems thrive on operational constancy. Upgrading mechanical handling equipment—particularly feed augers, rotary valves, and reactor seals—mitigates failure points that historically caused unexpected shutdowns. Predictive maintenance technologies, including infrared thermography and sensor-driven diagnostics, enable operators to forecast degradation trends before they escalate into critical faults. This foresight reduces downtime and stabilizes production scheduling.
Automation features also streamline man-hour requirements. Distributed control systems (DCS) and real-time analytics platforms oversee reactor temperature, pressure gradients, hydrocarbon flow rates, and emission parameters. Operators gain immediate visibility into deviations, permitting responsive corrective actions. Consistent operation improves both cost forecasting and contractual reliability, especially for facilities selling pyro-oil under forward agreements. Upgraded systems therefore create a more resilient business model.
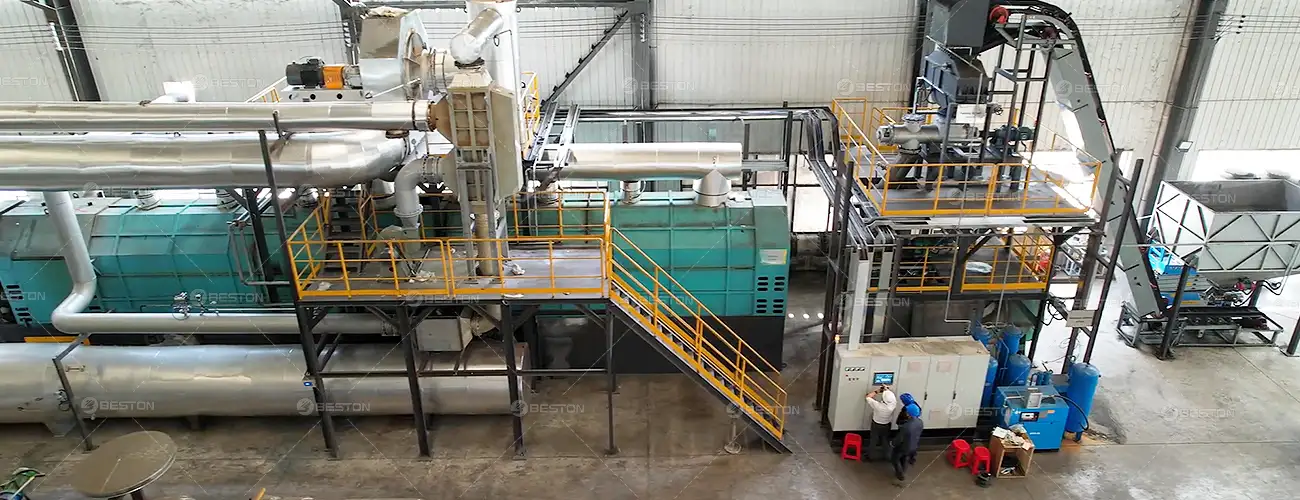

Positioning for Future Technological Integration
Incremental modernization prepares continuous pyrolysis systems for deeper integration with emergent circular economy technologies. Artificial intelligence–driven feedstock sorting, blockchain-based material tracking, and hybrid chemical recycling modules can all interface more effectively with upgraded infrastructure. Flexible reactor controls and modular hardware layouts facilitate these integrations without substantial retrofits.
In this evolving industrial landscape, the pyrolysis plant that adopts phased technological enhancements becomes more compatible with future industry standards. It gains adaptability, profitability, and environmental legitimacy. These attributes will define the next generation of plastic-to-resource facilities as global expectations shift toward cleaner and more sophisticated waste valorization methods.